Advocacy & Lobbying
Isocyanates
What is it?
Isocyanates are chemicals that can cause serious health problems when inhaled or in contact with skin. They can irritate the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract, and cause asthma and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Workers exposed to isocyanates can also become sensitized, meaning they can have severe reactions even at low levels of exposure. Some of the symptoms of isocyanate exposure include tear secretion, dry throat, cough, chest pain, difficulty breathing, and eye irritation
Isocyanates are chemicals which are used in the manufacture of polyurethane coatings (amongst other areas). Typical isocyanates used within the Coatings Industry include
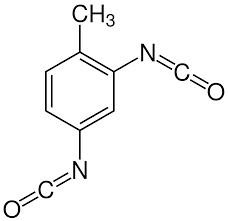
TDI (Toluene Diisocyanate) [CAS 91-08-7]
MDI (Methylene Diphenyl Diisocyanate) [CAS 101-68-8]
HDI (Hexamethylene Diisocyanate) [CAS 822-06-0]
Isophorone Diisocyanate [CAS 4098-71-9]
Within the Coatings industry, these are generally used as polymerised versions, but all will have some residual monomeric isocyanate remaining in the material, it is the residual monomeric material which causes the health effects.
It should be noted that isocyanate will also react with moisture in the atmosphere (hence moisture cured polyurethanes)
Why is EPA/Worksafe concerned about Isocyanates and related compounds?
Exposure to Isocyanates and related compounds is well known to result in skin and lung sensitization among workers and has been documented to cause asthma, lung damage, and in severe cases, fatal reactions.
While the majority of polyurethane products containing isocyanates and related compounds undergo “curing” (hardening) prior to reaching the consumers, some polyurethane products such as coatings, sealants and adhesives may be sold and used in an uncured form, increasing exposure risks for consumers.
This action is part of EPA/ Worksafe’s work to ensure chemical safety in order to protect human health.
In New Zealand as well as other jurisdictions, there is a mandatory requirement that when spraying products containing isocyanates, that air-fed respiration is worn, in addition to all other required Personal Protective Equipment [PPE].
Isocyanates have previously been assigned a Workplace Exposure Standard [WES], which indicates the allowable exposure for a human within a typical 8-hour working shift, as well as a Short Term Exposure Limit [STEL] which indicates an allowable exposure within any 15-minute period.
In 2022, Worksafe NZ proposed significantly reducing this WES/ STEL from the existing 0.02 mg/m³ / 0.07 mg/m³ limits to ones significantly lower [WES 0.0001 mg/m³|STEL 0.0005 mg/m³], these proposed values are below the current levels of detection
Following the Industry Consultation, these were left where they were, but it was noted that they would be reviewed again in 2023. In 2023 Industry meetings were proposed and later postponed to review these revised limits.
It is important that the Industry gets behind the Consultations, and puts their voice forward, to ensure that these new proposed limits are not introduced, as it will have significant effects on the painting/ floor coating industries.


![MDI (Methylene Diphenyl Diisocyanate) [CAS 101-68-8]](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/64af5024c1986c7ec3cb3b1e/21921206-5d14-408a-9e04-770f44bb5ed1/Methylene+Diphenyl+Diisocyanate.png)
![HDI (Hexamethylene Diisocyanate) [CAS 822-06-0]](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/64af5024c1986c7ec3cb3b1e/fcc344ab-eb2d-4bb8-8642-fb7d70a36ab0/Hexamethylene+Diisocyanate.png)
![Isophorone Diisocyanate [CAS 4098-71-9]](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/64af5024c1986c7ec3cb3b1e/9938fe3d-e1b5-4e29-a82a-a067453e9839/Isophorone+Diisocyanate.png)